Strategy is one of the four pillars of sustainability disclosure (governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets). An organization’s strategy is its plan for future performance, a road map to achieving the company’s basic long-term goals and objectives. Strategic planning examines the challenges to meeting those objectives and goals and determines what to do, how to do it, and why. A company’s resilience in addressing sustainability and climate-related risks is an important part of its strategy.
Two of the most common strategic approaches are transformation and growth (or expansion). Companies face constant change in their business environments—industries change, or societies and consumer preferences change, and thus companies must change their business models to succeed in new environments. These changes vary in intensity and may be more or less disruptive.
A transformation strategy may be necessary when the company is underperforming or facing disruption due to significant technological, environmental, social, or political changes. For example, global warming and higher temperatures are changing the demand for home heating in some parts of the world, impacting business models for energy companies, such as natural gas companies. At the same time, utility companies and energy providers have to adapt to changing regulations and are being pushed to make investments to shift to renewable power generation. Utility companies are responding to disruptive environmental and political changes.
On the other hand, a business can do well and not foresee disruptive events that would require a transformative strategy. In such instance, companies focus their strategy primarily on growing their market share in existing markets and expanding to other markets. Companies pursuing growth strategies may choose from a variety of approaches, such as expanding market share, improving profitability through innovation, customer retention through customer service, or diversification into new markets or new products.
INSIGHT “We want to be number one in all the markets in which we operate” is not a strategy—it’s a goal. A strategy includes a thoughtful plan for how the company will move forward.
An overview of the company’s strategy—its long-term goals and plans on how to reach them— helps executives and employees in the day-to-day management and provides a benchmark for the board’s oversight. It also helps investors, business partners, and other stakeholders to understand the company better and how it plans to create value.
A company’s future performance is critical for investors to understand, but most of the information companies report relates to past or current performance. Effective strategy disclosure can fill the information gap and give investors forward-looking and decision-useful information to draw their own conclusions.
Strategy information is usually at the front of a company’s annual report and is often called the strategic report or management report.
Management Overview
Typically, a letter from the CEO in the annual report includes the management overview of the strategy and an explanation of the progress and setbacks in implementing the strategy, along with any change of plans. It introduces the rest of the strategy report, including strategic objectives and key performance indicators, risks analysis, and the sustainability issues facing the company. Then it provides a high-level review of performance against the company’s targets and performance indicators. These letters help provide insight into the company’s accomplishments and where it is headed in the future.
Describe Your Long-term Strategy
Describe your company’s long-term strategy actions, how it conducts its activities, and the expected results and impacts. Explain how the strategy will capitalize on strengths and address weaknesses to ensure greater success and profitability.
Discuss Your Sustainability Strategy
Explain the company’s strategy for addressing significant sustainability-related risks and opportunities. Describe the impact of sustainability risks and opportunities affecting the company’s business model, value chain, and financial results.
ISSB IFRS S1 General Requirements for Disclosure of Sustainability-related Financial Information includes disclosure on strategy as one of the four pillars for sustainability disclosure (1. governance, 2. strategy, 3. risk management, and 4. metrics and targets). This strategy section of this platform is aligned with the main recommendations under the strategy pillar of the forthcoming draft. Please find below an excerpt from the standard for your reference.
-
ISSB IFRS S1 General Requirements For Disclosure Of Sustainability-related Financial Information (Excerpt)
STRATEGY
28. The objective of sustainability-related financial disclosures on strategy is to enable users of general purpose financial reports to understand an entity’s strategy for managing sustainability-related risks and opportunities.
29. Specifically, an entity shall disclose information to enable users of general purpose financial reports to understand:
(a) the sustainability-related risks and opportunities that could reasonably be expected to affect the entity’s prospects (see paragraphs 30–31);
(b) the current and anticipated effects of those sustainability-related risks and opportunities on the entity’s business model and value chain (see paragraph 32);
(c) the effects of those sustainability-related risks and opportunities on the entity’s strategy and decision-making (see paragraph 33);
(d) the effects of those sustainability-related risks and opportunities on the entity’s financial position, financial performance and cash flows for the reporting period, and their anticipated effects on the entity’s financial position, financial performance and cash flows over the short, medium and long term, taking into consideration how those sustainability-related risks and opportunities have been factored into the entityʼs financial planning (see paragraphs 34–40);
(e) the resilience of the entity’s strategy and its business model to those sustainability-related risks (see paragraphs 41–42).
Source: ISSB IFRS S1 General Requirements For Disclosure Of Sustainability-related Financial Information
The European Sustainability Reporting Standards: ESRS 2 General Disclosures includes disclosure on strategy as one of the four pillars for sustainability disclosure (1. governance, 2. strategy, 3. impact, risk and opportunity management, and 4. metrics and targets). This strategy section of this platform is aligned with the main recommendations under the strategy pillar of the forthcoming draft. Please find below an excerpt from the standard for your reference.
-
The European Sustainability Reporting Standards: ESRS 2 General Disclosures (Excerpt)
3. STRATEGY
37. This chapter sets disclosure requirements that enable an understanding of:
(a) the elements of the undertaking’s strategy that relate to or affect sustainability matters, its business model and its value chain;
(b) how the interests and views of the undertaking’s stakeholders are taken into account by the undertaking’s strategy and business model; and
(c) the outcome of the undertaking’s assessment of material impacts, risks and opportunities, including how they inform its strategy and business model.
Source: European Sustainability Reporting Standards: ESRS 2 General Disclosures.
Introduce your company’s strategy and the context necessary for readers to make informed assessments about it, including sustainability management. Tailor the reporting on strategy to the company’s material issues and strategic objectives.
Robust strategy disclosure can include the following (see figure below):
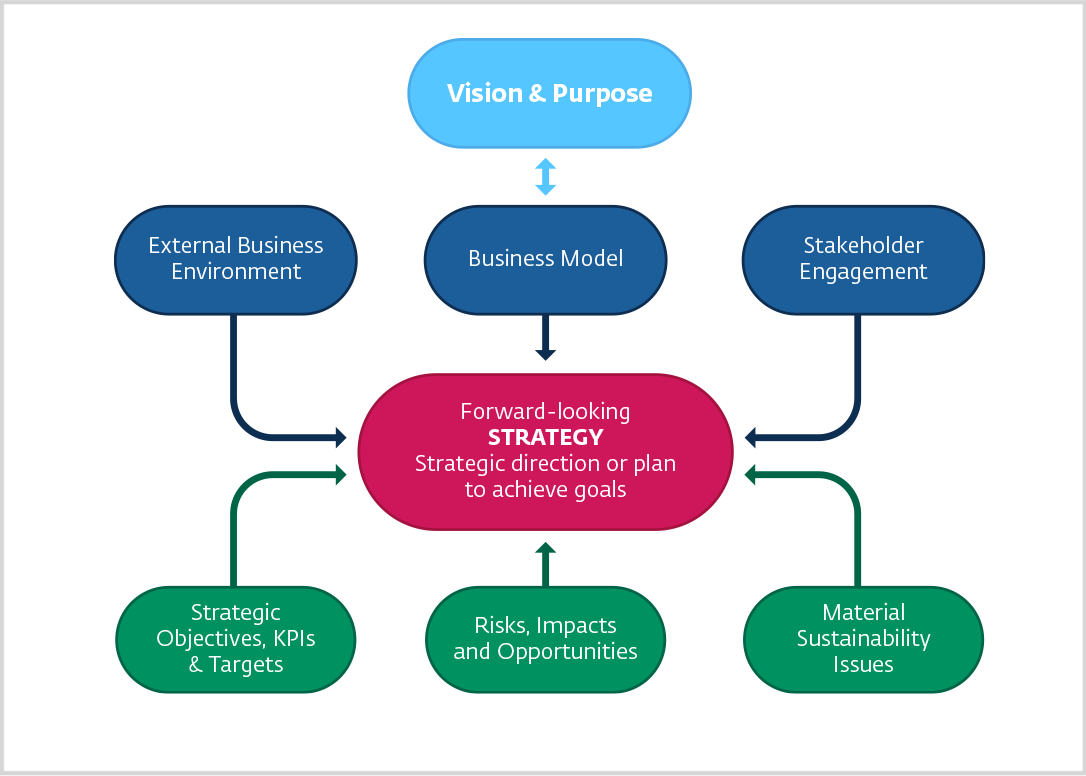
Source: IFC, 2023
- Description of company’s vision, including what it aims to achieve and purpose, why it aims to achieve it, and making sure there is a clear connection with the company strategy (in light blue);
- A clear description of the strategic vision, direction, or plan (often included in the CEO letter; in red in the figure);
- Insight into the business model, external environment, and stakeholders’ concerns and interests—the context that determines if a business strategy is the right strategy (in blue);
- Insights into the implementation process, strategic objectives, material sustainability risks and opportunities, key performance indicators and targets, and risk management that help readers understand whether the company is implementing the strategy properly and achieving results in strategic focus areas (in green).
Note: The rest of this section addresses guidance on the main elements of strategy reporting individually.






